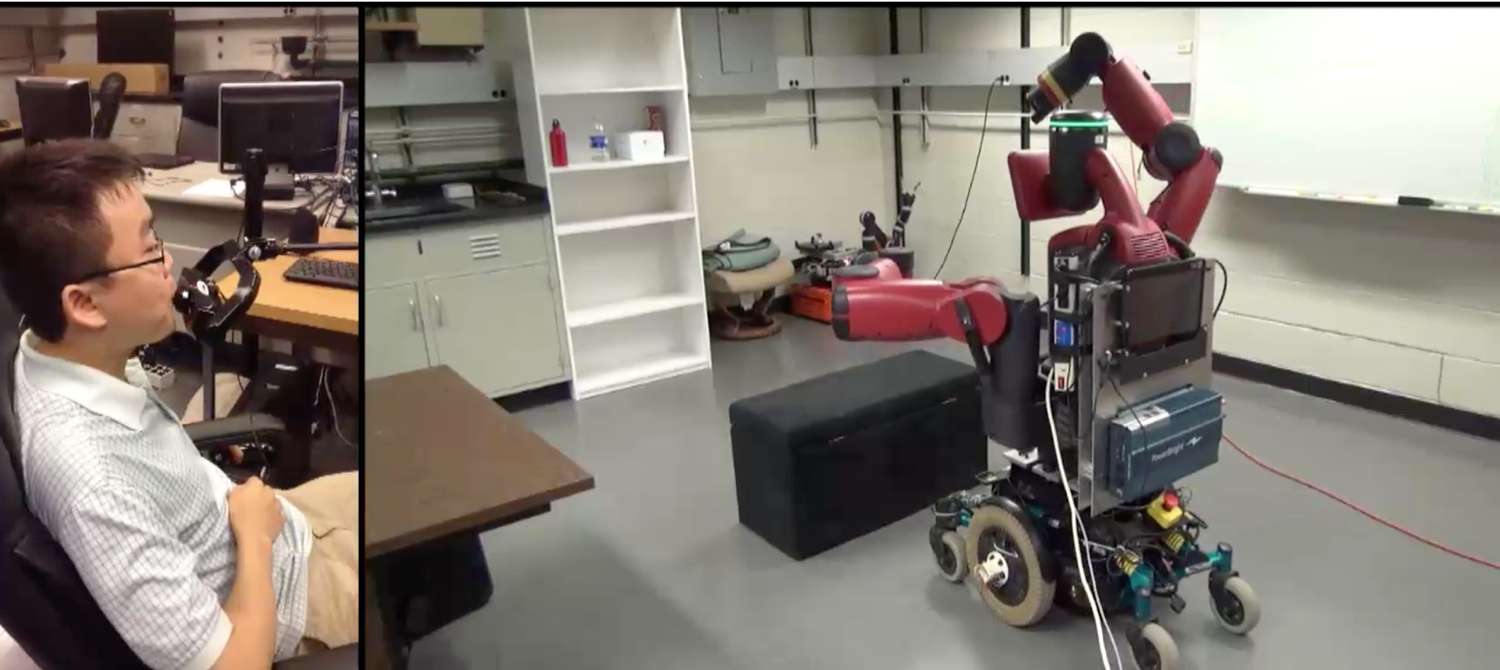
Persons with spinal cord injuries (SCI) at the fourth to seventh cervical vertebra (C4-C7) are often free of cognitive and speech and hearing impairments, but have no active lower body movement and limited movement of
their upper limbs and fingers. Thus they have many challenges performing activities of daily living (ADL). Our unique team of researchers from Tufts School of Engineering (Messner) and the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (Bedell, Everhart Skeels, Harney), and from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (Wen) in robotics, control systems, and occupational therapy (OT), is ideal for tackling this inherently interdisciplinary problem.
Project Videos: https://youtu.be/cPj3-gu9fbE, https://youtu.be/5JM8bgZvMg0
Robot Assistance with Activities of Daily Living for Persons with C4-C7 Spinal Cord Injury
Craig Nielsen Foundation
John Wen, jointly with Bill Messner, Gary Bedell, Sarah Skeels of Tufts University
This project will develop effective robotic assistance for individuals with C4-C7 SCI by investigating the appropriate balance between autonomous control and human teleoperation. The research will address three major types of operations in ADL: (1) motion in cluttered environment, (2) motion and force control, and (3) bi-manual (two-arm) robot operations. By integrating evaluation and feedback from users and therapists with technology enhancement (algorithms, information, and interface), our research will systematically improve collaboration between the human users and assistive robots. In addition, insights from human sensorimotor control will guide this assessment-improvement iteration. Our experience and complementary expertise at Tufts (and RPI) and existing equipment/infrastructure will ensure significant, impactful, and rapid progress. The data that we collect and the lessons learned will be used to develop proposals for significant follow-on funding from other sources, such at NIH, NSF, National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research (NIDILRR) and private foundations.